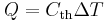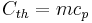Thermal mass
Thermal mass is a concept in building design which describes how the mass of the building provides "inertia" against temperature fluctuations, sometimes known as the thermal flywheel effect.[1] For example, when outside temperatures are fluctuating throughout the day, a large thermal mass within the insulated portion of a house can serve to "flatten out" the daily temperature fluctuations, since the thermal mass will absorb thermal energy when the surroundings are higher in temperature than the mass, and give thermal energy back when the surroundings are cooler, without reaching thermal equilibrium. This is distinct from a material's insulative value, which reduces a building's thermal conductivity, allowing it to be heated or cooled relatively separate from the outside, or even just retain the occupants' thermal energy longer.
Scientifically, thermal mass is equivalent to thermal capacitance or heat capacity, the ability of a body to store thermal energy. It is typically referred to by the symbol Cth and measured in units of J/°C or J/K (which are equivalent). Thermal mass may also be used for bodies of water, machines or machine parts, living things, or any other structure or body in engineering or biology. In those contexts, the term "heat capacity" is typically used instead.
Contents |
Background
The equation relating thermal energy to thermal mass is:
where Q is the thermal energy transferred, Cth is the thermal mass of the body, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
For example, if 250 J of heat energy is added to a copper gear with a thermal mass of 38.46 J/°C, its temperature will rise by 6.50 °C. If the body consists of a homogeneous material with sufficiently known physical properties, the thermal mass is simply the mass of material present times the specific heat capacity of that material. For bodies made of many materials, the sum of heat capacities for their pure components may be used in the calculation, or in some cases (as for a whole animal, for example) the number may simply be measured for the entire body in question, directly.
As an extensive property, heat capacity is characteristic of an object; its corresponding intensive property is specific heat capacity, expressed in terms of a measure of the amount of material such as mass or number of moles, which must be multiplied by similar units to give the heat capacity of the entire body of material. Thus the heat capacity can be equivalently calculated as the product of the mass m of the body and the specific heat capacity c for the material, or the product of the number of moles of molecules present n and the molar specific heat capacity 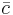 . For discussion of why the thermal energy storage abilities of pure substances vary, see factors that affect specific heat capacity.
. For discussion of why the thermal energy storage abilities of pure substances vary, see factors that affect specific heat capacity.
For a body of uniform composition, 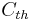 can be approximated by
can be approximated by
where 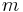 is the mass of the body and
is the mass of the body and 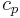 is the isobaric specific heat capacity of the material averaged over temperature range in question. For bodies composed of numerous different materials, the thermal masses for the different components can just be added together.
is the isobaric specific heat capacity of the material averaged over temperature range in question. For bodies composed of numerous different materials, the thermal masses for the different components can just be added together.
Thermal mass in buildings
Thermal mass is effective in improving building comfort in any place that experiences these types of daily temperature fluctuations—both in winter as well as in summer. When used well and combined with passive solar design, thermal mass can play an important role in major reductions to energy use in active heating and cooling systems. The terms heavy-weight and light-weight are often used to describe buildings with different thermal mass strategies, and affects the choice of numerical factors used in subsequent calculations to describe their thermal response to heating and cooling. In building services engineering the use of dynamic simulation computational modelling software has allowed for the accurate calculation of the environmental performance within buildings with different constructions and for different annual climate data sets. This allows the architect or engineer to explore in detail the relationship between heavy-weight and light-weight constructions, as well as insulation levels, in reducing energy consumption for mechanical heating or cooling systems, or even removing the need for such systems altogether.
Properties required for good thermal mass
Ideal materials for thermal mass are those materials that have:
- high specific heat capacity,
- high density
Any solid, liquid, or gas that has mass will have some thermal mass. A common misconception is that only concrete or earth soil has thermal mass; even air has thermal mass (although very little).
A table of volumetric heat capacity for building materials is available here, but note that their definition of thermal mass is slightly different.
Use of thermal mass in different climates
The correct use and application of thermal mass is dependent on the prevailing climate in a district.
Temperate and cold temperate climates
Solar exposed thermal mass
Thermal mass is ideally placed within the building and situated where it still can be exposed to low angle winter sunlight (via windows) but insulated from heat loss. In summer the same thermal mass should be obscured from higher angle summer sunlight in order to prevent over-heating of the structure.
The thermal mass is warmed passively by the sun or additionally by internal heating systems during the day. Thermal energy stored in the mass is then released back into the interior during the night. It is essential that it be used in conjunction with the standard principles of passive solar design.
Any form of thermal mass can be used. A concrete slab foundation either left exposed or covered with conductive materials e.g. tiles; is one easy solution. Another novel method is to place the masonry facade of a timber-framed house on the inside ('reverse-brick veneer'). Thermal mass in this situation is best applied over a large area rather than in large volumes or thicknesses. 7.5–10 cm (3-4") is often adequate.
Since the most important source of thermal energy is from the Sun, the ratio of glazing to thermal mass is an important factor to consider. Various formulas have been devised to determine this.[2] As a general rule, additional solar-exposed thermal mass needs to be applied in a ratio from 6-8:1 for any area of north facing (Southern Hemisphere) or south facing (Northern Hemisphere) glazing above 7% of the total floor area. For example a 200 m2 house with 20 m2 of north facing glazing has 10% of glazing by total floor area; 6 m2 of that glazing will require additional thermal mass. Therefore, 36-48 m2 of solar-exposed thermal mass is required. The exact requirements vary from climate-to-climate.
Thermal mass for limiting summertime over-heating
Thermal mass is ideally placed within a building where it is shielded from direct solar gain but exposed to the building occupants. It is therefore most commonly associated with solid concrete floor slabs in naturally ventilated or low energy mechanically ventilated buildings where the concrete soffit is left exposed to the occupied space.
During the day heat gains from the sun, the occupants of the building, and any electrical lighting and equipment, causes the air temperatures within the space to increase but this heat is absorbed by the exposed concrete slab above, thus limiting the temperature rise within the space to be within acceptable levels for human thermal comfort. In addition the lower surface temperature of the concrete slab also absorbs radiant heat directly from the occupants also benefiting their thermal comfort.
By the end of the day the slab has in turn warmed up, and now as external temperatures reduce the heat can be released and the slab cooled down ready for the start of the next day. However this "regeneration" process is only effective if the building ventilation system is operated at night to carry away the heat from the slab. In naturally ventilated buildings it is normal to provide automated window openings to faciltate this process automatically.
Hot, arid climates (e.g. desert)
This is a classical use of thermal mass. Examples include adobe or rammed earth houses. Its function is highly dependent on marked diurnal temperature variations. The wall predominantly acts to retard heat transfer from the exterior to the interior during the day. The high volumetric heat capacity and thickness prevents thermal energy from reaching the inner surface. When temperatures fall at night, the walls re-radiate the thermal energy back into the night sky. In this application it is important for such walls to be massive to prevent heat transfer into the interior.
Hot humid climates (e.g. sub-tropical and tropical)
The use of thermal mass is the most challenging in this environment where night temperatures remain elevated. Its use is primarily as a temporary heat sink. However, it needs to be strategically located to prevent overheating. It should be placed in an area that is not directly exposed to solar gain and also allows adequate ventilation at night to carry away stored energy without increasing internal temperatures any further. If to be used at all it should be used in judicious amounts and again not in large thicknesses.
Cold incoming tap water may be piped through radiators to draw summer thermal energy from the air. In most areas, its initial temperature is 60 °F (16 °C) degrees. Since the existing plumbing is deep underground, it's well insulated from the heat of the day.
Materials commonly used for thermal mass
- Water. Water has the highest volumetric heat capacity of all commonly used material. Typically, it is placed in large container(s), acrylic tubes for example, in an area with direct sunlight. It may also be used to saturate other types material such as soil to increase heat capacity.
- Clay Brick, Adobe brick or mudbrick. See Brick, Adobe.
- Earth, mud, and sod. Dirt's heat capacity depends on its density, moisture content, particle shape, temperature, and composition. Early settlers to Nebraska built houses with thick walls made of dirt and sod because wood, stone, and other building materials were scarce. The extreme thickness of the walls provided some insulation, but mainly served as thermal mass, absorbing thermal energy during the day and releasing it during the night. Nowadays, people sometimes use earth sheltering around their homes for the same effect. In earth sheltering, the thermal mass comes not only from the walls of the building, but from the surrounding earth that is in physical contact with the building. This provides a fairly constant, moderating temperature that reduces heat flow through the adjacent wall.
- Rammed earth. Rammed earth provides excellent thermal mass because of its high density, and the high specific heat capacity of the soil used in its construction.
- Natural rocks and stones. See Stonemasonry.
- Concrete, clay bricks and other forms of masonry. The thermal conductivity of concrete depends on its composition and curing technique. Concretes with stones are more thermally conductive than concretes with ash, perlite, fibers, and other insulating aggregates.
- Insulating concrete forms are commonly used to provide thermal mass to building structures. Insulating Concrete Forms or ICF provide the specific heat capacity and mass of concrete. Thermal Inertia of the structure is very high because the mass is insulated on both sides.
- Log is used as a building material to create the exterior, and perhaps also the interior, walls of homes. Log homes differ from some other construction materials listed above because solid wood has both moderate R-value (insulation) and also significant thermal mass. In contrast, water, earth, rocks, and concrete all have low R-values.[3]
Seasonal energy storage
If enough mass is used it can create a seasonal advantage. That is, it can heat in the winter and cool in the summer. This is sometimes called "Passive annual heat storage or PAHS". The PAHS system has been successfully used at 7000 ft. in Colorado and in a number of homes in Montana.
See also
References
- ^ Principles of eco-design
- ^ Chiras, D. The Solar House: Passive Heating and Cooling. Chelsea Green Publishing Company; 2002.
- ^ Thermal Mass - Energy Savings Potential in Residential Buildings
External links
- Ogdenmfg.com, Thermal conductivity and specific heat charts